The Business of Afro Music: Revenue Streams, Market Growth, and Global Impact
The business of Afro music generates billions in global revenue through streaming platforms, record labels, and live performances. African music industry was valued at $343 million in 2021 and is projected to grow to $500 million by 2025, while Afrobeats generated approximately $100 million in global revenue in 2023. Artists like Burna Boy, Wizkid, and Davido have transformed African music into a lucrative global enterprise.
African music represents one of the fastest-growing segments in the global entertainment industry. Record labels, streaming services, and concert promoters now recognize Afro music as a major revenue driver. Artists earn money through multiple channels including digital streaming, merchandise sales, live performances, and brand partnerships.
Market Size and Revenue Growth
Music streaming market in Africa is projected to grow by 7.71% (2024-2027) resulting in a market volume of US$513.20m in 2027. This growth reflects increasing smartphone penetration and improved internet connectivity across African countries. Recorded music revenues in SSA were up 24.7% YoY in 2023, primarily driven by paid streaming revenues, which grew 24.5% YoY.
Streaming platforms generate the largest revenue share for Afro music artists. Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube Music feature dedicated African playlists that expose artists to global audiences. Platforms like Spotify and Apple Music have global playlists, “African Heat”, “Naija Hits”, and “Afropop Rising”, that showcase African talent to international audiences.
Revenue Distribution Challenges
Revenue distribution remains uneven across the Afro music value chain. While Afrobeats generated approximately $100 million in global revenue in 2023, only an estimated 2% of that income actually flowed back into Nigeria—the epicenter of the genre. International record labels and distribution companies capture most earnings, leaving African artists with smaller revenue shares.
| Revenue Source | Percentage Share | Growth Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Streaming Platforms | 65% | 24.5% annually |
| Live Performances | 20% | 15% annually |
| Physical Sales | 10% | -5% annually |
| Licensing & Sync | 5% | 30% annually |
Key Players and Record Labels
Major record labels now invest heavily in African talent. Universal Music Deal with Nigeria’s Mavin label highlights the increasing allure of Africa’s cultural exports. International partnerships provide African artists with global distribution networks and marketing resources.
Leading African record labels include Mavin Records, Chocolate City, and Spaceship Entertainment. Chocolate City is a leading record label based in Nigeria, with operations in other parts of the continent such as Kenya, South Africa, and Ghana. These labels develop local talent while negotiating international partnerships.
Independent vs Major Label Artists
Independent artists and record labels in Africa can now match and surpass their counterparts in more developed markets. Digital distribution platforms allow independent artists to reach global audiences without traditional label support. Artists retain higher revenue percentages when they maintain ownership of their music rights.
Streaming and Digital Revenue
Digital streaming dominates Afro music revenue generation. Music streaming market will grow from $46.7 billion to $52 billion by 2025, with African artists capturing increasing market share. Streaming platforms pay artists based on play counts, subscriber numbers, and regional pricing structures.
Artists optimize streaming revenue through playlist placements, social media marketing, and fan engagement strategies. Successful artists like Burna Boy and Wizkid generate millions of streams monthly across multiple platforms. Each platform offers different payout rates, with Spotify typically paying $0.003 to $0.005 per stream.
| Platform | African Users (Millions) | Payout Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Spotify | 8.2 | $0.004 per stream |
| Apple Music | 5.1 | $0.007 per stream |
| YouTube Music | 12.5 | $0.002 per stream |
| Boomplay | 95.0 | $0.001 per stream |
Live Performance and Concert Revenue
Concert performances generate substantial revenue for established Afro music artists. Artists like Wizkid, Davido, Burna Boy and Rema have captured the attention of the world, headlining international festivals. Festival appearances at Coachella, Glastonbury, and Rolling Loud command six-figure performance fees.
African music festivals create additional revenue opportunities for artists. Events like Afro Nation, Detty Rave, and Lagos Music Conference attract international audiences and sponsors. Artists earn money through ticket sales, merchandise, and brand sponsorships during these events.
Touring Economics
International touring provides the highest profit margins for successful Afro music artists. Tour revenue includes ticket sales, merchandise, VIP packages, and sponsorship deals. Artists typically split touring revenue with booking agents (10-15%), managers (15-20%), and production costs (30-40%).
Brand Partnerships and Sponsorships
Brand partnerships create lucrative revenue streams for Afro music artists. Companies like Pepsi, MTN, and Nike sponsor African artists to reach younger demographics. Endorsement deals range from $50,000 for emerging artists to millions for established stars like Davido and Wizkid.
Artists monetize their social media influence through sponsored content and product placements. Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter provide platforms for artists to promote brands while earning additional income. Successful campaigns generate revenue based on follower counts, engagement rates, and campaign objectives.
Music Publishing and Royalties
Music publishing generates long-term revenue for Afro music creators. Artists earn royalties when their songs play on radio, television, streaming platforms, and live venues. Performing rights organizations like COSON (Nigeria) and SAMRO (South Africa) collect and distribute royalty payments to rights holders.
Sync licensing provides additional revenue opportunities when Afro music appears in movies, TV shows, commercials, and video games. How to Create Afra Music guides help artists understand music creation processes that maximize licensing potential.
Copyright and Intellectual Property
Protecting intellectual property rights remains critical for Afro music business success. Artists register their works with copyright organizations to secure legal protection and revenue collection. Proper registration enables artists to earn royalties from global music usage and prevents unauthorized sampling.
Technology and Innovation
Technology platforms transform how Afro music artists conduct business. Digital distribution services like DistroKid, TuneCore, and CD Baby allow artists to upload music to all major streaming platforms simultaneously. Blockchain technology creates new revenue models through NFTs and cryptocurrency payments.
Artificial intelligence helps artists analyze streaming data, predict hit songs, and optimize marketing campaigns. Music recommendation algorithms on streaming platforms influence which African songs reach global audiences. Artists who understand these technologies gain competitive advantages in the marketplace.
Regional Market Differences
Different African regions generate varying revenue levels for music artists. Nigeria leads with the highest streaming numbers and international recognition. South Africa follows with strong Amapiano and house music exports. Ghana, Kenya, and Tanzania represent emerging markets with growing revenue potential.
Currency fluctuations affect artist earnings when international platforms convert payments to local currencies. Artists often prefer payments in US dollars or Euros to avoid exchange rate losses. Some platforms offer currency hedging options to protect artist revenues.
Investment and Funding
Investment in African music businesses attracts international venture capital and private equity firms. Music streaming platforms, record labels, and artist management companies receive funding to expand across African markets. Learning to Play Afro Music programs create educational opportunities that support industry growth.
Government initiatives support music industry development through grants, tax incentives, and infrastructure investments. Countries like Nigeria, South Africa, and Ghana create policies that encourage music entrepreneurship and export growth.
People Also Ask
Afro music artists earn between $0.001 to $0.007 per stream depending on the platform. Spotify pays approximately $0.004 per stream, while Apple Music pays around $0.007. Artists need millions of streams to generate substantial revenue from streaming alone.
Only about 2% of Afrobeats global revenue returns to Africa, according to recent industry reports. Most earnings flow to international record labels, distribution companies, and streaming platforms based outside the continent.
Nigeria generates the highest music revenue in Africa, followed by South Africa and Ghana. Nigeria’s Afrobeats exports drive most international earnings, while South Africa leads in domestic consumption and live performance revenue.
African artists attract international labels through streaming success, social media presence, and live performance skills. Labels scout talent on platforms like Spotify, YouTube, and TikTok. Artists need consistent releases, growing fan bases, and professional representation to secure major label deals.
Market Challenges and Opportunities
Piracy continues to affect Afro music revenue generation across African markets. Illegal downloading and streaming reduce artist earnings and discourage investment in local talent. However, improved internet infrastructure and smartphone adoption create new opportunities for legitimate music consumption.
Payment processing challenges limit how artists receive international earnings. Banking restrictions and high transaction fees reduce artist revenues from global platforms. Fintech solutions and cryptocurrency payments offer potential solutions to these challenges.
Infrastructure Development
Recording studio infrastructure improvements support higher-quality Afro music production. Professional recording facilities in Lagos, Johannesburg, and Accra attract international artists and producers. Traditional African Instruments integration with modern production techniques creates unique sonic signatures that appeal to global audiences.
Future Growth Projections
Industry analysts predict continued growth for the Afro music business sector. Rising smartphone penetration, improved internet connectivity, and growing international recognition drive market expansion. There’s still so much potential for Afrobeats and Amapiano in the coming years.
Emerging genres like Amapiano from South Africa and Afro-fusion create new revenue opportunities. Artists who innovate while maintaining cultural authenticity position themselves for long-term success. Afro Music Festivals provide platforms for discovering and promoting new talent.
Educational and Training Programs
Music business education programs help African artists understand industry economics and revenue optimization. Universities and private institutions offer courses in music entrepreneurship, digital marketing, and rights management. Afra Music Improvisation Tips for Beginners and similar resources support artistic development alongside business skills.
Professional development workshops teach artists about contract negotiation, intellectual property protection, and financial management. These programs create more informed artists who make better business decisions and retain higher percentages of their earnings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Afro music artists generate revenue through streaming platforms (65%), live performances (20%), physical sales (10%), and licensing deals (5%). Streaming provides the most consistent income, while concerts offer the highest profit margins per event.
Top Afrobeats artists like Burna Boy, Wizkid, and Davido earn between $5-15 million annually through combined revenue streams. Their income includes streaming royalties, concert fees, brand endorsements, and music publishing rights.
Apple Music pays the highest per-stream rates at $0.007, followed by Spotify at $0.004. However, Spotify and YouTube Music have larger African user bases, potentially generating more total revenue despite lower per-stream payments.
African music festivals like Afro Nation and Detty Rave pay headlining artists $100,000-500,000 per performance. Festivals also provide merchandise sales opportunities, fan base expansion, and networking with international music industry professionals.
African artists face challenges including uneven revenue distribution, limited access to international markets, piracy, payment processing difficulties, and lack of music business education. However, digital platforms increasingly level the playing field.
Authentic African rhythms differentiate artists in the global marketplace and create distinctive sounds that appeal to international audiences. Artists who master traditional rhythms while incorporating modern production techniques achieve the greatest commercial success.
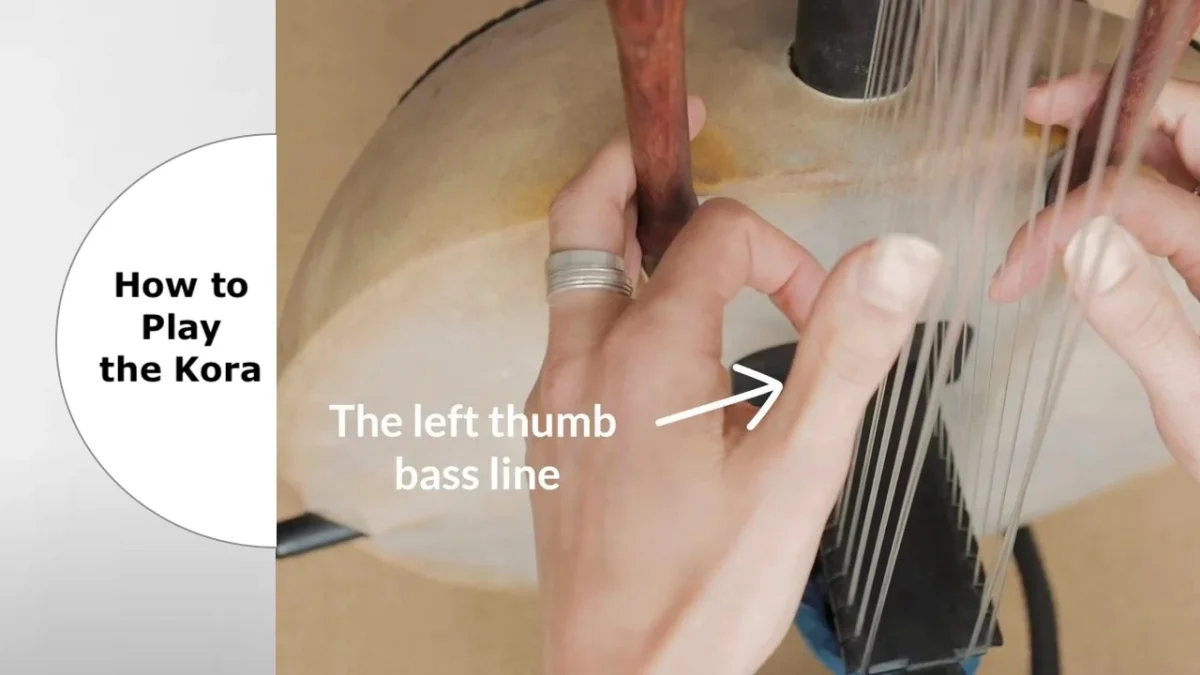
Traditional instruments add cultural authenticity that increases music licensing value and attracts international collaborations. Artists who incorporate instruments like the kora, talking drum, and mbira create unique sounds that command premium rates in sync licensing deals.