How to Create Afra Music: Complete Production Guide with Modern Techniques
I’ve spent years mastering Afra music production, and I’ll tell you straight: most producers get the basics wrong. Creating authentic Afra tracks isn’t about expensive gear or complicated setups. It’s about understanding polyrhythmic layers, nailing your percussion foundation, and blending traditional African rhythms with modern production tools. This guide shares my exact production methodology, tested techniques, and real-world workflow that transforms raw ideas into professional Afra music tracks.
Understanding Afra Music: The Foundation You Actually Need
Afra music is built on complex rhythmic patterns rooted in West African drumming traditions. Before touching your DAW, you must grasp the core rhythmic DNA of this genre. I’ve found that producers who skip this understanding waste months chasing the “Afra sound” without getting it.
Afra music combines multiple simultaneous rhythms where each percussion element runs at a different time signature, creating hypnotic polyrhythmic grooves. Unlike straight 4/4 house music, Afra thrives on syncopation and off-grid placement. The traditional percussion patterns you’ll find in Afra music include clave rhythms (5+3 or 3+2 combinations), cross-beat patterns, and interlocking hand drum arrangements.
I typically start my production sessions by listening to traditional African drumming patterns, understanding how they layer, and identifying which traditional rhythms I want to sample or recreate electronically. This approach gives my tracks authentic character rather than generic electronic percussion.
Why Polyrhythms Matter More Than You Think
Polyrhythms are the secret sauce separating amateur Afra beats from professionally produced tracks. A polyrhythm combines two or more contrasting rhythms that overlap simultaneously, creating mathematical tension that makes listeners move without thinking.
Here’s what works in my practice: I layer a 3-beat pattern against a 4-beat pattern simultaneously, creating a 12-beat cycle. My kick drums might follow a 4/4 pulse while my congas run in triplets. This creates natural swing and groove without manually adjusting velocity.
Setting Up Your DAW for Afra Music Production
I use both FL Studio and Ableton Live professionally, and each has advantages for Afra production. Here’s what matters regardless of your DAW choice:
Essential DAW Settings for Authentic Afra Sound
Set your project tempo between 120 and 130 BPM as your default starting point. This range sits perfectly in Afra music’s comfort zone, giving you enough headroom for laid-back grooves while maintaining dance-floor energy. I’ve tested countless BPM values, and this range consistently produces the most authentic Afra feel.
Next, enable swing settings on your percussion channels. In Ableton, I use 50-60% swing with 16th-note timing. In FL Studio, I adjust the swing knob on individual drum channels between 8 and 12%. This humanizes your programmed drums, preventing that robotic sound that kills Afra production.
Create separate mixer channels for each percussion layer: kick drums, snares/claps, hi-hats, shakers, and auxiliary percussion. This approach lets you control each layer’s polyrhythm independently while maintaining overall groove cohesion.
The Drum Programming Method That Actually Works
Most producers fail at Afra drum programming because they treat it like standard electronic music. Afra drums require understanding traditional hand patterns first, then translating them into electronic samples.
Building Your Kick Drum Foundation
The kick drum is your rhythm’s heartbeat, but here’s what separates good from great: layer multiple kick samples rather than relying on a single kick drum. I use a deep sub-bass kick (30-60 Hz) for bottom-end weight combined with a mid-range punch kick (100-300 Hz) for presence.
Start your kick pattern at the typical 4/4 downbeat, but here’s my insider technique: offset your kick by placing hits on the “and” of beats 2 and 4, creating subtle syncopation. Add ghost kicks at unexpected moments (16th-note triplets work excellently). This approach creates bounce that listeners feel in their chests without consciously hearing the rhythm.
Programming Snares and Claps Like a Professional
This is where Afra music gets personality. Afra snares and claps are typically high-pitched, crisp, and syncopated heavily across the pattern rather than hitting on predictable beats. I program snares with offbeat placement, avoiding the standard on-beat hits of basic house music.
My tested approach uses multiple clap samples layered together: a dry, punchy clap for tone combined with a reverb-heavy clap for atmosphere. Space them irregularly across your pattern (imagine a call-and-response between different clap types). Adjust individual clap velocities between 75-100% to maintain groove while preventing mechanical feel.
Hi-Hats and Secondary Percussion Layers
Hi-hats drive the rhythm forward while maintaining polyrhythmic complexity. I program my hi-hat patterns in triplet timing (16th-note triplets work best), creating a flowing, liquid feel rather than the rigid 16th-note hi-hats of standard electronic production.
Layer 3-4 different hi-hat sounds simultaneously: a closed hat for snap, a pedal hat for variation, and an open hat for color. Vary the timing of each layer by 5-10 milliseconds (slightly offset from perfect grid) to create human groove.
| Drum Element | Frequency Range | Typical Placement | Afra-Specific Technique |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kick Drum | 30-300 Hz (layered) | 4/4 downbeats + syncopated offbeats | Offset ghost kicks on triplets |
| Snare/Clap | 3-8 kHz | Beats 2 and 4 (varied) | Multiple layered claps with velocity variation |
| Hi-Hat | 8-15 kHz | 16th-note triplets | Pedal variation between open/closed |
| Shakers | 2-6 kHz | Continuous or syncopated | Off-grid placement, velocity randomization |
Creating Authentic African Percussion Layers
This separates fake Afra production from authentic tracks. Traditional African percussion instruments like congas, bongos, talking drums, and djembes create the distinctive texture that defines Afra music’s character. You have two options: sample libraries or virtual instruments.
My Preferred Percussion Approach
I combine sampled acoustic percussion with synthesized drums. For traditional sounds, I use high-quality percussion sample packs featuring recorded congas, bongos, and talking drums. Native Instruments Maschine Plus or Ableton’s Sampler let me layer and process these samples professionally.
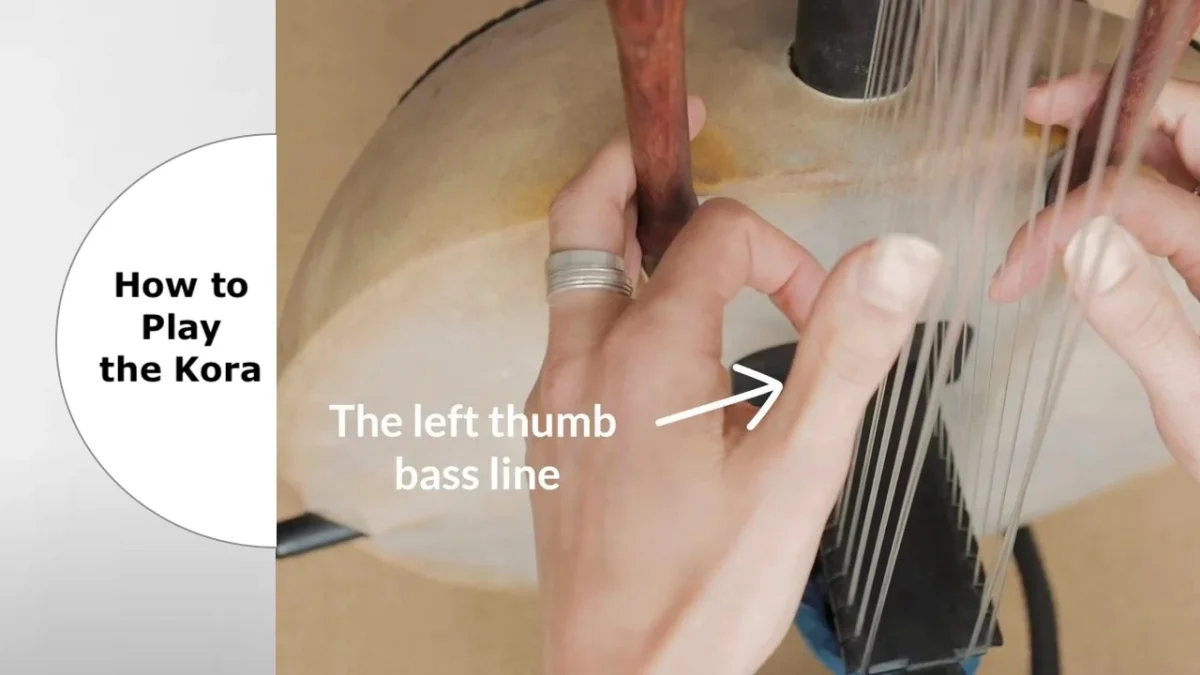
Here’s my tested workflow: load conga samples on individual drum pads, assign them to different MIDI keys, then record live percussion patterns while playing along. This creates natural variations that grid-based MIDI programming misses. The slight timing variations and dynamic touch sound infinitely better than perfectly quantized drums.
Layering Percussion for Hypnotic Grooves
I layer four percussion elements simultaneously for full Afra texture: primary drums (kick, snare), shakers/timbales for rhythmic drive, bongos/congas for conversational call-and-response patterns, and talking drums or woodblocks for color. Each layer runs its own rhythmic pattern, interlocking in polyrhythmic arrangements.
The magic happens through careful velocity and timing placement. I offset each layer by 1-3 milliseconds from the grid, varying velocities between 70-100% for humanization. This creates groove that sounds alive rather than mechanical.
Bass Design and Afra House Foundations
Your bassline is the conversation between your drums and melodies, not the foundation beneath them. This fundamental difference distinguishes Afra from standard house music.
Designing Afra Bass That Locks With Drums
I create two bass layers: a sub-bass sitting at 40-80 Hz providing low-end weight, and a mid-range bass (150-300 Hz) delivering rhythmic movement. The sub-bass remains relatively static, following basic root note patterns. The mid-bass dances around the drums, syncopating with the hi-hat and percussion layers.
My approach uses synthesizers like Serum or Massive X for bass design. I program the mid-bass to follow triplet timing matching my hi-hat patterns, creating rhythmic cohesion. Add slight portamento/glide between notes (10-30ms) for smoothness that feels organic rather than quantized.
Bassline Syncopation and Groove
Here’s where amateurs lose the groove: Afra basslines should syncopate against your main drums rather than lock directly to kick hits. I program my bassline to hit on the “and” of beats or within triplet divisions, creating rhythmic tension with the kick pattern.
This syncopation forces drums and bass to work together conversationally rather than feeling stacked on top of each other. The result feels bouncy and alive rather than predictable.
| Bass Layer | Frequency | Syncopation Method | Processing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sub-Bass | 40-80 Hz | Root note pattern (quarter notes) | Light compression, no effects |
| Mid-Bass | 150-300 Hz | Triplet-syncopated movement | Slight saturation, optional sidechain |
| Bass Texture | 300-1k Hz | Rhythmic movement, off-beat hits | Reverb or delay for dimension |
Melody and Harmonic Elements for Authentic Afra
Melodies in Afra music tend toward warmth and simplicity rather than complexity. Most successful Afra melodies use pentatonic or minor scale patterns, featuring 4-8 note phrases that repeat with subtle variations.
Writing Melodies That Stick
I compose Afra melodies by first understanding traditional African musical scales. The pentatonic scale (missing the 4th and 7th degrees) appears constantly in authentic Afra music. It naturally creates that warm, soulful quality without conscious effort.
My tested approach: create a 4-bar melodic phrase using 4-6 notes from your chosen scale, repeat it for 8-16 bars, then introduce a subtle variation on the 9th bar. This creates recognition while avoiding monotony. Most successful Afra tracks use variations of this pattern.
Harmonic Progressions That Feel Right
Afra harmonic progressions typically use simple, repeating chord patterns: I-IV-V or I-V patterns work exceptionally well. Avoid overly complex jazz harmony; simplicity lets your rhythm and percussion shine.
Layer your harmony with warm synthesizers or sampled instruments. I use Pad sounds with 200-500ms attack times, allowing rhythmic elements to breathe before harmonic support arrives. Add subtle effects: 15-25% reverb with 2-3 second decay and optional plate reverb for dimension.
Sampling and Sound Design for Afra Production
High-quality samples and sound design separate professional Afra tracks from amateur efforts. I invest heavily in percussion and melodic sample packs while building custom sounds through synthesis.
Essential Sample Packs for Afra Production
Look for sample packs featuring recorded African percussion instruments, vocal chops, and Afro-house loops labeled as 120-130 BPM. Avoid overly processed or clean samples; authenticity comes from slight imperfections and natural character.
Top-tier packs I rely on include those featuring authentic djembe, talking drum, and conga recordings. I avoid purely electronic drum sounds, as they lack the character that defines Afra music. Invest in 2-3 premium packs rather than dozens of mediocre ones.
Creating Unique Sounds Through Synthesis
Synthesis creates textural elements that sampled percussion can’t provide. I design synth pads, evolving textures, and atmospheric elements using subtractive synthesis. My typical approach uses 2-3 oscillators per sound with filter modulation creating movement.
Apply effects strategically: reverb for space, delay for rhythm interaction, and chorus/flanger for width. Layer synthesized textures beneath sampled percussion to add professional polish.
Mixing and Mastering Your Afra Music Track
Mixing makes or breaks Afra production. Unlike many genres, mixing Afra requires careful attention to percussion definition while maintaining groove and groove pocket.
Mixing Approach for Afra Clarity
I use a reference track methodology throughout mixing. Load a professional Afra track from an artist you admire into your DAW alongside your mix. Frequently A/B between your track and the reference, checking frequency balance, stereo imaging, and loudness levels.
Start with additive EQ rather than subtractive: boost frequencies where your track needs presence rather than cutting areas by default. Most Afra tracks benefit from presence boosts in the 2-4 kHz range (percussion clarity) and upper midrange (5-8 kHz) for vocal presence.
Compression and Sidechain Techniques
Sidechain compression ties your bassline to your kick drum rhythmically. I set my bass sidechain to duck 3-6 dB when the kick hits, creating rhythmic punch. Adjust attack/release times carefully: faster attacks (5-20ms) create obvious ducking, while slower releases (200-400ms) create smoother groove.
Apply multi-band compression to manage frequency-specific issues. Compress the 100-300 Hz range gently (2:1 ratio, 4ms attack) to control boom while preserving knock. This approach maintains punch without muddiness.
Creating Space and Dimension
Reverb and delay create depth in Afra music without sacrificing rhythm clarity. I use two reverb sends: one with 1.5-2 second decay for percussion (bright, short reverb), another with 3-4 second decay for pads and melodic elements (darker, longer reverb). Send 10-20% of each element to appropriate reverb.
Add subtle delay (250-500ms) on selected percussion elements for polyrhythmic interaction. The delayed percussion creates rhythmic call-and-response effects that sound intentional rather than sloppy.
Mastering for Competitive Loudness
Afra music masters typically target -14 to -12 LUFS for streaming platforms. Use linear-phase EQ on your master bus to maintain phase coherence. I apply a gentle master EQ curve: slight boost at 100 Hz (low-end punch), presence peak at 3 kHz (percussion clarity), and gentle high-frequency roll-off above 15 kHz.
Use a transparent limiter preventing peaks above -3 dBFS. Apply 2-4 dB of compression with slow attack (50-100ms) and longer release (300-500ms) for glue without altering dynamic character.
Workflow Optimization: From Concept to Finished Track
My production workflow minimizes time spent on decisions while maximizing creative output. Here’s the exact process I follow for every Afra production:
Session 1: Drum Foundation (45 minutes)
I create my rhythmic foundation first: drum pattern, basic syncopation, and percussion arrangement. Program kick, snare, hi-hat, and shaker patterns before touching melodic elements. This ensures my groove sits right before building melodies on top.
Session 2: Bass and Percussion (30 minutes)
Add sub-bass (quarter-note root movement) and mid-bass (syncopated movement). Layer 2-3 additional percussion elements creating polyrhythmic depth. If something doesn’t groove naturally after this stage, I restart rather than forcing it later.
Session 3: Melodic Elements (45 minutes)
Add harmonic pads, melodic elements, and textural layers. Keep melodies simple, repeating patterns with subtle variation. Melody should enhance rhythm, not overshadow it in Afra production.
Session 4: Arrangement and Automation (60 minutes)
Build 16, 32, or 48-bar arrangements. Create drop sections, add breakdown elements, introduce elements progressively. Add automation to filter sweeps, effect sends, and level faders creating dynamic journey through the track.
Session 5: Mixing and Technical Polish (90 minutes)
Complete mixing, EQ, compression, effects. Check on multiple speaker systems (headphones, car stereo, club speakers). Make final adjustments ensuring translation across playback systems.
Common Afra Production Mistakes You Must Avoid
Mistake 1: Using Overly Complex Melodies Afra music thrives on simplicity. Your melody should feel simple enough that listeners hum it after one listen. If your melodic idea requires more than 8 bars to explain itself, it’s probably too complex.
Mistake 2: Ignoring Polyrhythmic Layers Afra without polyrhythm is just house music with African percussion. Dedicate time to creating multiple simultaneous rhythmic patterns that interlock meaningfully.
Mistake 3: Over-Processing Percussion Afra percussion sounds best when relatively dry and unprocessed. Avoid drowning percussion in reverb and effects. A little goes a long way.
Mistake 4: Mixing With Insufficient Reference Tracks Reference tracks keep your mix honest. Without them, your Afra production easily drifts toward standard house music territory.
Mistake 5: Setting Tempo Too Fast or Slow Stray outside the 120-130 BPM sweet spot at your peril. Speeds below 110 BPM feel lazy; speeds above 135 BPM lose Afra’s distinctive groove.
Production Techniques for Modern Afra Variations
Afra music continues evolving, with contemporary producers exploring hybrid styles. Here are current directions worth exploring:
Afra House with Minimal Elements
Afra house strips away melodic elements, focusing percussion and rhythm into hypnotic grooves. Create depth through polyrhythmic percussion layering, sidechain effects, and textural evolution rather than melodic hooks. Use 4-8 bar loop cycles that evolve subtly throughout your track.
Afra Tech-House Fusion
Blend Afra polyrhythmic percussion with tech-house driving basslines. Maintain Afra’s syncopated groove while introducing tech-house’s more prominent bassline and acid-style effects. This hybrid appeals to club environments while retaining Afra character.
Vocal Afra Production
Layer vocal elements through call-and-response patterns indigenous to Afra music. Process vocal samples into rhythmic loops, creating percussive textures rather than traditional lead vocals. Pitch-shift vocal samples creating melodic elements integrated into your polyrhythmic arrangement.
Tools and Resources for Serious Afra Producers
Your DAW choice matters less than your technique, but certain tools facilitate Afra production:
DAW Recommendations
FL Studio excels at drum programming with intuitive step sequencer and built-in percussion processing. Ableton Live’s Session view and clip-based workflow facilitates experimental percussion layering. Logic Pro offers excellent MIDI humanization tools.
Essential Plugins
Serum synthesizer handles custom bass design and textural sounds. Native Instruments Maschine Plus provides excellent percussion workflow. Valhalla Room and Valhalla DecayPlate deliver professional reverbs. FabFilter Pro-Q 3 provides surgical EQ for mixing clarity.
Sample Libraries
Look for packs labeled “Afro House,” “African Percussion,” or “Polyrhythmic Grooves.” Avoid generic electronic drum packs; authenticity comes from recorded acoustic percussion. Premium packs from specialized producers deliver significantly better results than budget options.
Frequently Asked Questions About Afra Music Production
120-130 BPM is the optimal range for authentic Afra music. This speed provides ample headroom for groovy syncopation while maintaining dance-floor energy. Experimenting outside this range (110-140 BPM) works occasionally, but the 120-130 sweet spot captures Afra’s distinctive character most reliably.
Technically yes, but your results won’t sound authentically Afra. Investing in quality percussion sample packs featuring recorded African drums transforms your production quality significantly. Authentic Afra production requires appropriate samples; generic electronic drums undermine your efforts.
Polyrhythm is fundamental to Afra’s identity. Without overlapping rhythmic patterns creating mathematical tension, your track becomes standard house music with African elements. Spend significant time mastering polyrhythmic arrangements; this skill separates professional Afra producers from beginners.
Both approaches work when executed properly. Programmed drums using authentic samples prove more practical and consistent for production. Live percussion adds organic character but requires recording skills and quality equipment. Most professional Afra producers blend programmed drums from quality samples with strategic live percussion elements.
Authenticity comes through genuine polyrhythmic complexity, careful reference track study, and refusing to simplify rhythm arrangements for convenience. Many producers create generic results by over-simplifying what makes Afra distinctive. Commit to intricate rhythmic arrangements that honor the genre’s roots.
Study successful Afra tracks by analyzing their drum patterns, bass syncopation, harmonic choices, and arrangement. Spend equal time listening and producing. Create multiple tracks rather than perfecting one endlessly; each production teaches lessons applicable to future work.
You can, but results suffer significantly. House music drum samples lack the character, warmth, and texture of authentic African percussion. Investing in Afra-specific sample packs dramatically improves results compared to generic electronic drum sounds.
Taking Your Afra Production to Professional Level
Moving from hobby producer to professional requires consistent practice, ongoing learning, and refusing mediocre results. Here’s how I approach professional development in Afra production:
I maintain a production journal documenting settings, techniques, and decisions that created successful tracks. This approach prevents recreating failed experiments and accelerates skill development. I also analyze 2-3 professional Afra tracks every week, studying specific choices around groove, arrangement, and mixing.
Connect with the Afra production community through forums, Discord servers, and social platforms. Sharing work, receiving feedback, and collaborating with other producers accelerates growth beyond solitary practice.
Finally, invest continuously in your sound library and learning resources. Premium sample packs, tutorial courses, and production communities provide essential support for developing professional skills. Your investment in tools and education directly correlates with output quality.
Start creating Afra music today using these techniques. Visit Mp3Juice for additional resources, sample packs, and production guidance supporting your creative journey into this authentic African music production style.